



Next: Descriptions of Files and
Up: How to Make a
Previous: Running the Model
The standard QTCM1 package includes pre-written scripts, routines,
and control files that utilize standard FORTRAN 77,
NCAR Graphics or GrADS to plot
the time series of selected output fields.
These files are found in directory proc.
The FORTRAN 77 and NCAR Graphics programs require compilation before
being used for the first time. These include:
- checkdata.f
- FORTRAN program to find out how many time
levels QTCM1 output files q.out or qmean.out contain.
- xy.f
- NCAR Graphics program that creates a
gmeta file from the file timeseries.out
that can be viewed by
idt or ctrans.
To create this command,
compile xy.f using FORTRAN with links to selected NCAR Graphics
libraries.
The GrADS scripts provided do not need to be compiled; just
execute them within the GrADS program.
The output files from QTCM1 provide GrADS
binary (Fortran sequential unformatted) data.
Note that in GrADS, for 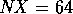 ,
, 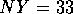 , over global
longitude and latitude
, over global
longitude and latitude 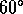 S to
S to 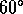 N,
grid box (1,1) of the output is located at
longitude
N,
grid box (1,1) of the output is located at
longitude 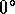 E, latitude
E, latitude 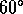 S.
Some of the GrADS scripts and control files provided with
with the QTCM1 tar package include:
S.
Some of the GrADS scripts and control files provided with
with the QTCM1 tar package include:
- o.ctl
- This control file is configured for monthly output
from a 10-year run forced with climatological SST. Note that
this file assumes the output is produced on a machine using
``big-endian'' format (e.g. SUN).
- qtcmpar.gs
- Script for defining QTCM1 parameters used in
calculating surface wind, etc.
- clim16yr.gs
- Calculates climatology of a variety of fields for
a 16-year run with output given every 30 days. Climatological
fields are denoted by attaching a ``c'' to the end of the field
name, e.g. ``
precc'' for climatology
of ``prec'', the precipitation. To use clim16yr.gs,
qtcmpar.gs must be present in the same directory.
- anom16yr.gs
- Calculates anomalies of a variety of fields for
a 16-year run with output given every 30 days. Anomaly
fields are denoted by attaching an ``a'' to the end of the field
name, e.g. ``
preca'' for anomaly
of ``prec'', the precipitation. This script requires
clim16yr.gs be run first.
- dump.gs
- This script creates a file called ``meta'' which
contains ``quick and dirty''
January and July climatology plots for essentially
every field output. Requires output from a 16-year run
with output given every 30 days. To create a Postscript file
from ``meta,'', type in the command
gxps -i meta -o fname
where fname is the name
of the Postscript file being created.
A few other useful examples of GrADS scripts are also included in
the QTCM1 distribution. For example, flux.gs defines various
fluxes; precEQ.gs was used to plot Figure 16 in Zeng et al.
[2].
All the scripts listed above require that you first open a GrADS control
file before use. GrADS scripts end with the extension
``gs'', while GrADS control files end with ``ctl''.
For more information on the output file formats, see
Section 1.4.2.




Next: Descriptions of Files and
Up: How to Make a
Previous: Running the Model
Johnny Wei-Bing Lin
Wed Aug 26 16:58:31 PDT 1998